Data Minimization: A Strategic Approach to Secure and Efficient Data Management
In today’s data-driven world, managing personal information responsibly is crucial. Data minimization, a fundamental principle in data privacy and protection, is about collecting and retaining the minimum amount of personal information necessary for legitimate purposes and for the shortest duration possible. It’s akin to packing for a trip: Instead of lugging around a bulky suitcase filled with unnecessary items, you select and pack only what’s essential for your journey.

Understanding Data Minimization
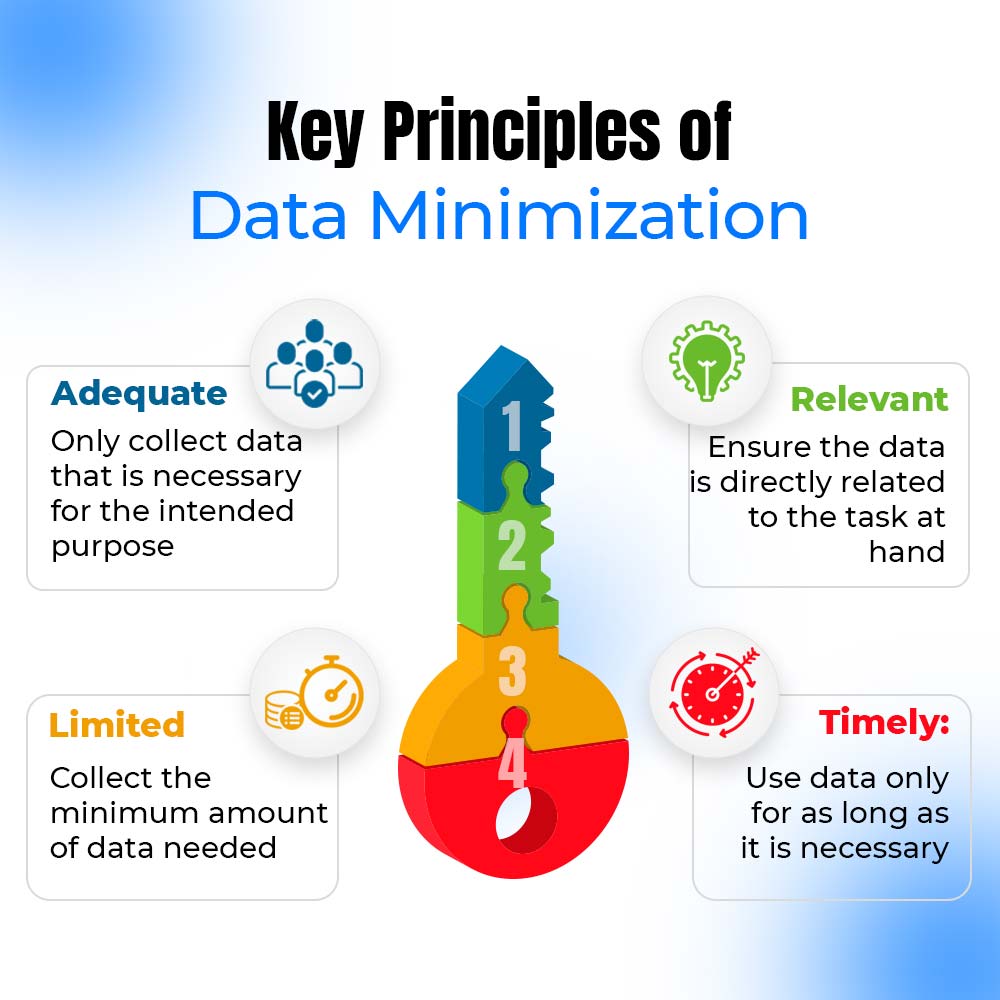
At its core, data minimization involves four main operations:
- Selective Data Collection: Only gather information that is necessary for your specific purposes, ensuring that you avoid collecting any irrelevant or excessive data from the outset.
- Timely Data Deletion: Establish clear timelines for data retention and ensure that information is deleted promptly once it is no longer needed for its intended purpose, reducing the risk of data breaches.
- Tokenization: Replace sensitive information such as names, emails, phone numbers, and social security numbers with non-sensitive equivalents or tokens to protect personal data while maintaining its utility.
- Data Redaction: Use techniques like masking partial data fields, such as displaying only the last four digits of a credit card number, to protect sensitive information without compromising the usability of the data.
By being selective about the personal information collected and processed, organizations can reduce privacy and regulatory risks. Imagine packing lightly for a trip it makes the journey smoother and easier. Similarly, data minimization lightens the burden of managing unnecessary information, reducing the impact of potential breaches and making recovery more manageable.
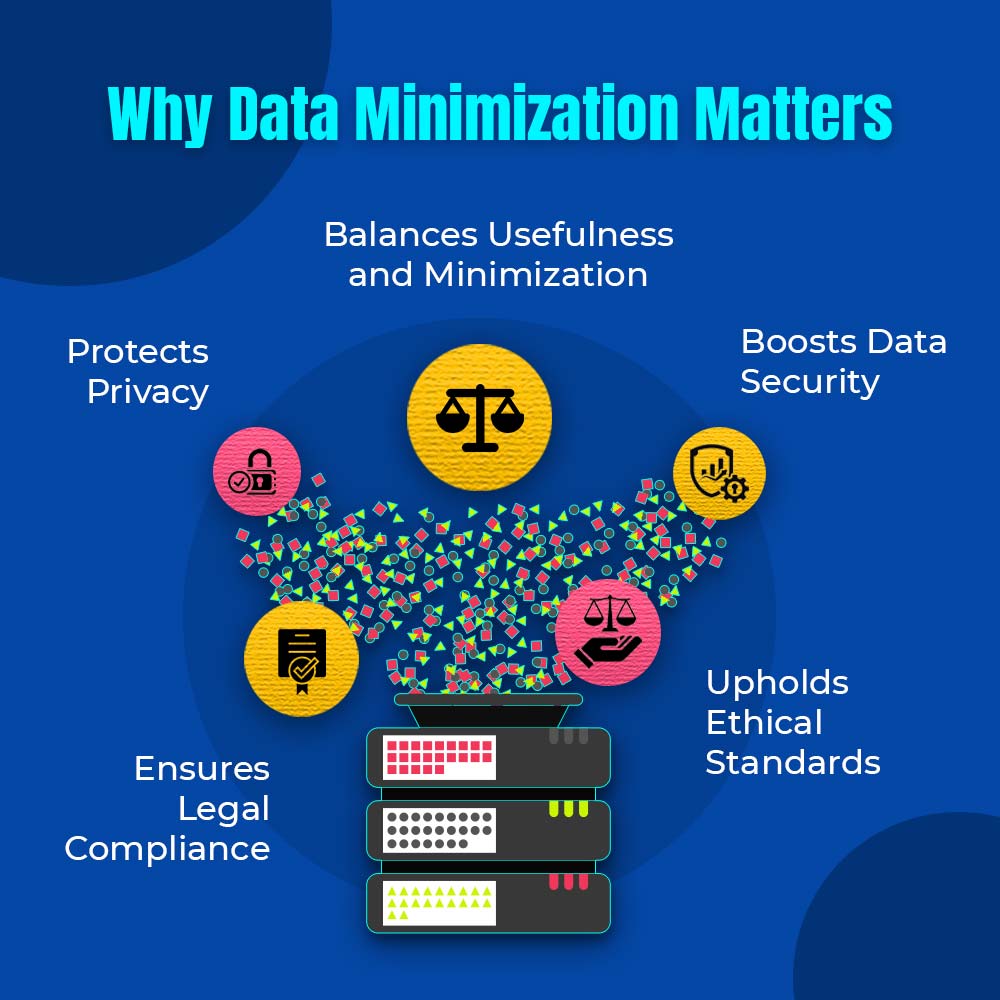
The Importance of Data Minimization
Understanding the importance of data minimization is the first step toward a more secure, ethical, and privacy-conscious digital landscape. Here’s why it’s crucial:
- Reducing Privacy Risks: By limiting the amount of data collected, organizations significantly reduce the risk of data exposure. Collecting only necessary data minimizes the chances of sensitive information being compromised in a breach, thereby protecting customer privacy.
- Promoting Ethical Data Usage: Practicing data minimization fosters trust and credibility, as it demonstrates a commitment to protecting individual privacy and using data ethically. It encourages transparent data practices and reinforces an organization’s reputation for integrity and responsibility.
- Reducing Legal Liability: Holding less data minimizes opportunities for data breaches and privacy violations, which can lead to costly legal repercussions and regulatory fines. Compliance with data protection regulations is more straightforward when only essential data is collected and retained.
- Cost Savings: Storing and processing large volumes of data can be expensive. By minimizing data collection, organizations can significantly cut operational expenses related to data storage, processing, and maintenance, resulting in more efficient resource allocation and reduced overhead costs.
GDPR and Data Minimization Principles

Data minimization is not just a best practice; it is a key requirement under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). GDPR mandates that organizations must be transparent about the data they collect and only use it for specified purposes. It requires companies to clearly communicate data collection practices to users, often through privacy policies and cookie banners.
A notable example is the British Airways data breach in 2019, where the personal and financial details of approximately 500,000 customers were compromised due to inadequate security measures and excessive data retention. The company was fined $222.89 million for violating GDPR principles, including data minimization. This incident underscores the importance of adhering to data minimization practices to avoid severe penalties.
Implementing Data Minimization in Your Organization
Implementing data minimization is a systematic and ongoing process.
Here’s a structured approach:
- Data Mapping and Assessment: Conduct a thorough assessment of the data you collect, identifying its sources and the specific purposes for which it is processed. This helps in understanding the data landscape and determining areas where minimization can be applied.
- Review Data Collection: Scrutinize existing data collection processes to ensure they are necessary and transparent. Evaluate whether each piece of data collected is essential for achieving your objectives.
- Clear Consent Management: Implement robust mechanisms to obtain informed and explicit consent from individuals, ensuring they are aware of what data is being collected and for what purposes.
- Data Retention Policies: Define and implement clear policies for how long data should be retained based on its necessity. Regularly review and update these policies to ensure they align with current data protection standards and organizational needs.
- Anonymization: Use techniques to remove personally identifiable information (PII) from datasets while maintaining their utility. Anonymization helps in protecting privacy without sacrificing the functionality of the data.
- Regular Data Audits: Continuously assess compliance with data minimization principles through regular audits. These audits help identify areas for improvement and ensure ongoing adherence to best practices.
- Training and Documentation: Educate staff on data minimization principles and maintain detailed documentation of policies and procedures. Regular training ensures that employees are aware of and can implement data minimization practices effectively.
- Ongoing Commitment: Recognize data minimization as a continuous process that requires ongoing attention and adaptation. Stay informed about changes in data protection regulations and emerging best practices to ensure compliance and enhance data security.
Data Minimization Techniques
Data minimization involves various techniques to handle data responsibly:
- Data Masking: Protect sensitive information within datasets by replacing it with fictitious but structurally similar data. This ensures that sensitive data is obscured while still allowing for legitimate use.
- Data Retention Policies: Establish clear policies for how long different types of data will be retained and ensure prompt deletion when no longer needed. These policies help manage data lifecycles and reduce unnecessary data storage.
- Consent Management: Implement mechanisms for individuals to provide and manage their consent preferences. Clear consent management ensures that data collection and processing are transparent and aligned with user expectations.
- De-Identification/Anonymization: Remove personally identifiable information (PII) from datasets while retaining data utility. De-identification helps protect privacy without compromising the usefulness of the data.
- Tokenization: Replace sensitive information with tokens that reference the original data stored securely. Tokenization minimizes the presence of sensitive data within systems and reduces the risk of data exposure.
- Data Encryption: Protect data by converting it into ciphertext using encryption algorithms. Encryption ensures that data remains secure both in transit and at rest, safeguarding it from unauthorized access.
Business Benefits of Data Minimization
Data minimization offers several key advantages for businesses:
- Data Democratization: Anonymized data can be shared more freely within the organization, promoting collaboration and faster decision-making. Teams can access and analyze essential information without compromising individual privacy, enhancing business agility.
- Simplified Business Operations: Streamlined data collection and retention simplify operations across various departments. By handling only necessary data, organizations can improve efficiency, reduce administrative burdens, and focus resources on core business activities.
- Strengthened Data Privacy: Reducing the amount of data collected minimizes the risk of data breaches, enhancing customer trust. Organizations that prioritize data minimization demonstrate a commitment to protecting personal information, fostering long-term customer relationships.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to data minimization principles helps organizations comply with regulations like GDPR and CCPA. Compliance with these regulations reduces legal risks and potential fines, ensuring that data practices meet the highest standards.
- Improved Customer Trust: Customers feel safer knowing their data is handled responsibly. Organizations that practice data minimization build a reputation for integrity and transparency, which can lead to increased customer loyalty and satisfaction.
- Reduced Impact of Data Breaches: In the event of a breach, having less data exposed means less damage and easier recovery. Data minimization limits the amount of sensitive information at risk, mitigating the consequences of security incidents.

Technical Benefits of Data Minimization
Technically, data minimization offers several advantages:
- Privacy By Design: Embedding privacy principles into system architecture reduces the risk of data exposure. Data minimization ensures that privacy is considered at every stage of data handling, from collection to processing and storage.
- Enhanced Data Security: Minimizing data collection makes it easier to implement strong security measures. With less data to protect, organizations can focus on securing critical information more effectively.
- Faster Response to Data Requests: With less data to sift through, organizations can respond more quickly to information requests. This efficiency improves customer service and operational responsiveness.
- Lower Costs for Storing and Managing Big Data: Reducing the data footprint cuts storage and processing expenses, leading to significant cost savings. Organizations can allocate resources more efficiently and reduce overhead costs associated with managing large volumes of data.
Conclusion
Data minimization is a strategic approach to managing data responsibly. By collecting and retaining only what is necessary, organizations can protect individual privacy, reduce legal risks, and enhance operational efficiency. Embracing data minimization fosters trust, promotes ethical data usage, and ensures compliance with data protection regulations, ultimately contributing to a more secure and privacy-conscious digital landscape.