Navigating the AI Renaissance: Implications, Innovations, and Ethical Considerations
In the era of the AI Renaissance, marked by immense innovation potential, there also looms substantial risk. Hence it becomes extremely important to discuss the implications of AI. A notable incident unfolded in 2023 when Altman faced a lawsuit from a collective of AI researchers, alleging infringement upon their intellectual property rights.
This ongoing legal battle has brought forth crucial inquiries into the profound implications of AI concerning issues of ownership, liability, and ethical considerations. As the case continues, it serves as a focal point for exploring the intricate intersection of technology and legal and ethical frameworks.
As we delve deeper into the uncharted territories of this technological frontier, the progression of AI has evoked a spectrum of emotions, ranging from awe to apprehension.
This article seeks to dissect the multifaceted implications of AI, meticulously examining not only its potential benefits but also the challenges it presents. By navigating through these intricacies, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the ever-evolving landscape shaped by artificial intelligence.
Autonomous Vehicles:
In the realm of autonomous vehicles, self-driving cars employ advanced AI algorithms, empowering them to perceive their surroundings, make decisions, and navigate safely sans human intervention.


A comprehensive report by Allied Market Research revealed that the global autonomous vehicle market, valued at $76.13 billion in 2020, is anticipated to soar to $2,161.79 billion by 2030. This projection reflects a staggering Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 40.1% from 2021 to 2030, underscoring the rapid evolution of this transformative technology.


Natural Language Processing (NLP):
The field of Natural Language Processing (NLP) a total branch of AI focusing on the interaction between computers and human language, has witnessed remarkable strides. Chatbots, virtual assistants, and voice recognition systems have become increasingly sophisticated in comprehending and responding to natural language.
Gartner’s predictions are indicative of this progression, forecasting that Conversational AI will lead to an $80 billion reduction in contact center agent labor costs by 2026. These advancements in NLP not only streamline communication but also pave the way for more efficient and intuitive human-computer interactions.
Healthcare and Medical Diagnosis:
AI is reshaping the landscape of healthcare, ushering in a revolution in medical diagnosis, drug discovery, and patient care. Deep learning algorithms, capable of analyzing vast medical datasets, contribute to more accurate and timely diagnoses.
A study published by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) exemplifies the potential of AI in healthcare, demonstrating its ability to diagnose skin cancer. This heralds a new era where AI-powered tools assist healthcare professionals in early disease detection, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes and care.
Examples of AI-driven healthcare solutions and their benefits
Google Health:
Google Health, functioning as a personal health record (PHR), consolidates users’ medical information in one accessible repository. Leveraging AI, Google Health provides personalized health insights, such as tracking weight and blood pressure over time, exemplifying the fusion of technology and individualized healthcare.
IBM Watson for Oncology:
IBM Watson for Oncology stands as an AI-powered system designed to empower oncologists to make well-informed treatment decisions. By analyzing a patient’s medical history, tumor data, and other pertinent factors, Watson for Oncology identifies optimal treatment options, showcasing the potential of AI in personalized and data-driven healthcare.
Enlitic:
Enlitic, a pioneering company in the realm of AI, focuses on software development for early cancer detection. Their innovative software can analyze medical images, including mammograms and CT scans, to identify potential cases of cancer. This underscores the transformative role of AI in augmenting diagnostic capabilities and improving the efficacy of healthcare services.
Robotics and Automation:
The International Federation of Robotics reported a historic milestone in 2021, with a record-setting 517,385 new industrial robots installed globally in factories. This surge reflects the accelerating adoption of automation technologies worldwide.
A noteworthy aspect of this evolution is the rise of collaborative robots, or cobots, working seamlessly alongside humans to enhance productivity and efficiency. The automotive industry, claiming a 31% share in 2021, stands as the leading customer for the robotics industry in India, as outlined by BusinessWire.
The integration of AI-powered automation not only streamlines processes but also reduces errors, enabling businesses to optimize their operations for enhanced competitiveness.
Personalized Recommendations:
AI algorithms have become adept at analyzing extensive datasets to deliver personalized recommendations, exemplified by platforms like Netflix, Spotify, and Amazon. Leveraging AI, these platforms offer content or products tailored to individual user preferences and behavior, creating a more engaging and personalized user experience.
As AI continues to automate tasks across various industries, its impact on the job market emerges as a multifaceted issue. The dual implications of AI on employment include the potential for job displacement as machines and algorithms assume tasks once performed by humans. However, it also opens avenues for the creation of new jobs, as businesses necessitate skilled professionals to develop, maintain, and operate AI systems. Navigating this delicate balance between automation and job creation poses a challenge, highlighting the need for proactive strategies to adapt to the evolving dynamics of the workforce.
Automation and Job Displacement:
AI-powered automation stands as a transformative force with the potential to streamline processes, boost efficiency, and cut costs across various industries. An illustrative example is the deployment of AI-powered chatbots to address customer queries, a development that may pose challenges for traditional customer service roles, potentially leading to job displacement.


The “Future of Jobs 2022″ report from the World Economic Forum (WEF) paints a nuanced picture, projecting that automation could displace approximately 75 million jobs by 2022. However, it also anticipates the creation of 133 million new roles due to industrialization, resulting in a net loss of 58 million jobs. Industries such as manufacturing, transportation, customer service, and data entry are identified as particularly susceptible to automation, underlining the need for strategic workforce planning.
AI as a Collaborative Tool: Job Transformation and New Opportunities
Contrary to being a mere substitute for human labor, AI emerges as a collaborative tool, augmenting human productivity and decision-making. While automation may render certain job roles obsolete, it simultaneously paves the way for new opportunities and transforms existing ones.
AI technology has the potential to enhance human capabilities, enabling workers to focus on intricate and creative tasks that demand critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
As routine tasks undergo automation, there is a burgeoning demand for workers equipped with AI-related skills, including data analysis, programming, and AI system development. Adapting to these changes and fostering a culture of upskilling or reskilling within the workforce is pivotal to harnessing the benefits of AI and ensuring a seamless transition into the evolving job landscape.


Examples of How AI Augments Human Capabilities and Enhances Productivity:
Data Analysis:
- AI facilitates advanced data analysis, allowing professionals to derive meaningful insights from vast datasets, leading to more informed decision-making.
Programming Assistance:
- AI tools assist in programming tasks, accelerating the development process and reducing the margin for errors.
AI System Development:
- The creation and enhancement of AI systems involve human expertise, underscoring the collaborative nature of AI in technological advancements.
Creative Tasks:
- AI supports creative endeavors by automating routine aspects, enabling individuals to focus on the inventive and imaginative aspects of their work.
In Healthcare:
one of the implications of AI is a pivotal role in healthcare by augmenting human capabilities and enhancing productivity. AI-powered imaging tools contribute significantly to early cancer detection, providing doctors with advanced diagnostic support. Additionally, AI-powered chatbots streamline communication, enabling doctors to respond swiftly and accurately to patient queries.
IBM’s Watson for Oncology exemplifies this, empowering oncologists to make informed treatment decisions by analyzing a patient’s medical history, tumor data, and other factors to identify optimal treatment options.
In Manufacturing:
The manufacturing sector benefits from AI-powered robots that handle repetitive and challenging tasks, enhancing efficiency and safety. These robots can also monitor production lines for defects, contributing to quality control. Google’s DeepMind has developed an AI-powered system aiding factory workers in identifying and addressing product defects.
Utilizing computer vision, this system not only identifies weaknesses but also provides recommendations for improvement, showcasing the collaborative synergy between AI and human expertise.
In Customer Service:
AI-powered chatbots in customer service streamline interactions by addressing common queries promptly, leaving more complex questions to be handled by human representatives. This not only improves response times but also allows human agents to focus on intricate and personalized customer interactions, ultimately enhancing overall service quality.
In Finance:
Finance benefits from AI-powered trading algorithms that analyze extensive data sets to identify trading opportunities and execute trades automatically. Goldman Sachs, for instance, employs an AI-powered system leveraging machine learning to analyze historical market data. This system aids traders in making more informed investment decisions by identifying potential opportunities and risks, showcasing AI’s role in enhancing financial decision-making.
In Journalism:
The New York Times employs AI to aid journalists in finding and verifying information. The AI-powered system utilizes natural language processing to analyze text, identifying potential sources of information. This not only expedites the information-gathering process but also assists journalists in maintaining accuracy and credibility in their reporting.
In Marketing:
AI proves invaluable in marketing by tracking customer behavior and preferences. It predicts which customers are most likely to be interested in specific products or services, enabling targeted and personalized marketing campaigns. This data-driven approach enhances marketing efficiency and improves the overall customer experience.
In Product Development:
AI is instrumental in product development, simulating customer interactions with new products and identifying potential areas for improvement. This accelerates the innovation process, ensuring products are refined based on insights gained through AI-driven simulations, ultimately meeting customer expectations more effectively.
In Risk Management:
Risk management benefits from AI’s ability to analyze vast datasets, identify potential risks and develop predictive models. This proactive approach enhances the identification and mitigation of risks, contributing to more effective risk management strategies.
Job Creation and Economic Growth:
While automation may lead to the displacement of specific jobs, it simultaneously stimulates job creation in emerging fields. Advancements in AI technology foster the development, maintenance, and improvement of AI systems, giving rise to new employment opportunities. The growth of AI-related industries, encompassing machine learning, data analytics, and robotics, contributes to economic growth and productivity gains.
A study by PwC titled “The Future of Jobs 2022” underscores this potential, indicating that AI can create more jobs than it displaces. The study projects the creation of 133 million new roles by 2022, while replacing 75 million jobs, resulting in a net job creation of 58 million.
In response to the evolving AI landscape, six key job roles are highlighted for exploration in 2023:
1. AI Ethics Officer:
In an era emphasizing the importance of ethics in AI, AI Ethics Officers play a crucial role. They ensure the ethical development and use of AI systems, addressing potential concerns and promoting transparency and fairness.
2. AI Product Manager:
AI Product Managers bridge technology and market demands, overseeing the development and successful launch of AI-powered products. Collaboration with stakeholders and defining product requirements are central to their responsibilities.
3. AI Consultant:
AI Consultants provide expert guidance to businesses, identifying AI opportunities, developing strategies, and guiding organizations in implementing AI solutions. Their expertise spans various AI technologies and practical applications.
4. AI Architect:
AI Architects design and oversee the implementation of AI systems, working closely with stakeholders to define requirements, develop robust architectures, and ensure seamless integration. Strong expertise in scalable AI solutions is a key requirement.
The Bureau of Labor Statistics anticipates a 22% growth in AI-related occupations from 2020 to 2030, surpassing the average for all occupations. Whether pursuing roles like AI engineer, data scientist, researcher, or consultant, AI careers offer diverse opportunities across industries like healthcare, finance, and retail.
Effect of AI on the Economy:
According to the McKinsey Global Institute report, “Notes from the AI Frontier: Modeling the Impact of AI on the World Economy,” AI holds substantial potential for delivering economic benefits. By 2030, AI could contribute approximately $13 trillion to global GDP, translating to an annual growth of around 1.2%. However, the report highlights insights into the challenges and implications of AI adoption.
The economic benefits of AI are expected to be unevenly distributed, with leading AI countries capturing an additional 20 to 25% in net financial gains compared to present levels. Developing countries may experience a more modest increase of about 5 to 15%.
AI’s transformative power will generate 95 million new jobs by 2030, fostering economic growth. However, it may also displace around 800 million jobs, necessitating proactive measures for retraining and upskilling the workforce.
Ethical considerations, including bias, privacy, and potential job displacement, become crucial as AI evolves. Policymakers and businesses must proactively navigate these challenges, understanding that the impact of AI will vary based on a country’s development level, education system, and regulatory environment.
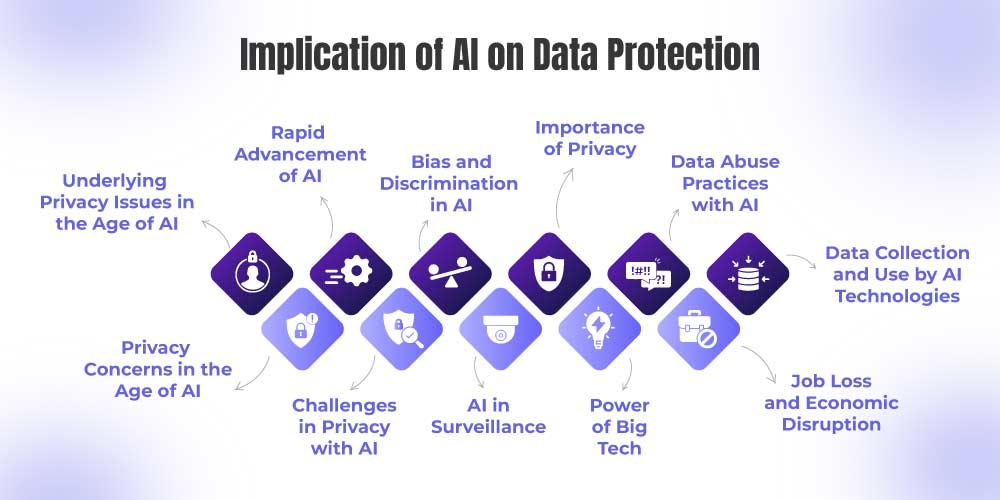

Implication of AI on Data Protection:
1. Rapid Advancement of AI:
The dynamic progression of AI reshapes daily life, from generative AI creating content to smart home devices’ learning habits. This accelerated evolution signifies a transformative era in human-technology interaction.
2. Privacy Concerns in the Age of AI:
With a surge in online data, privacy concerns become paramount. The growth of digital footprints underscores the need to examine AI’s impact on personal data and privacy, requiring a balance between technological advancement and individual privacy rights.
3. Importance of Privacy:
Privacy, a fundamental human right, safeguards individuals from harm and preserves autonomy. In the digital landscape, the significance of privacy amplifies, necessitating vigilant protection.
4. Challenges in Privacy with AI:
AI algorithms introduce challenges, from potential privacy violations and bias to discrimination and data abuse. A nuanced approach is crucial to ensure responsible and ethical AI use, addressing multifaceted concerns.
5. Bias and Discrimination in AI:
AI’s biased conclusions, rooted in training data, threaten privacy, especially in areas like biased job applications. Recognizing this link is vital for crafting solutions that promote fairness, equality, and privacy.
6. Job Loss and Economic Disruption:
AI’s efficiency brings job displacement concerns, potentially compelling individuals to disclose personal information for livelihood. Balancing economic shifts, job loss, and privacy requires an ethical approach to AI implementation.
7. Data Abuse Practices with AI:
AI capabilities open avenues for malicious data abuse, from fake media dissemination to sophisticated phishing attacks. Robust measures are imperative to counteract such abuses and protect individual privacy.
8. Underlying Privacy Issues in the Age of AI:
Invasive surveillance, unauthorized data collection, and Big Tech’s influence unveil underlying privacy issues. Vigilant regulation and oversight are essential to navigate these challenges and uphold privacy rights.
9. Power of Big Tech:
Big Tech’s unprecedented power raises implications for data influence, societal shaping, and political sway. Ethical data practices, transparency, and inclusivity are essential in technology and information dissemination.
10. Data Collection and Use by AI Technologies:
AI’s appetite for personal data amplifies privacy concerns. Transparent protocols, robust data security, and ethical design principles are imperative to instill confidence and uphold privacy standards.
11. AI in Surveillance:
AI in surveillance holds promise for law enforcement but raises concerns about privacy and civil liberties. Transparency, stringent regulation, and independent oversight are essential for balancing societal benefits with individual privacy rights.
Ethical Considerations With AI:
The rise of AI in 2023 brings forth ethical considerations that demand proactive measures to mitigate risks and safeguard individuals. One significant concern is:
1. Bias and Discrimination:
Unethical AI design and training can perpetuate biases, leading to discrimination against specific groups. An AI-powered hiring system, for instance, might unintentionally favor one gender or ethnicity, exacerbating existing inequalities in various sectors.
2. Violations of Privacy and Human Rights:
AI systems, capable of collecting and analyzing vast amounts of personal data, pose a threat to individuals’ privacy and human rights if misused. Tracking systems, in particular, have the potential to invade personal space and compromise autonomy, necessitating robust safeguards.
3. Unintended Harm:
Inadequately designed or tested AI systems, especially those involved in critical decision-making or autonomous operations, can lead to unintended harm. Systems intended to enhance safety may pose risks, resulting in accidents or adverse outcomes that endanger lives rather than safeguard them.
4. Weaponization of AI:
The development of AI for military purposes raises profound ethical concerns, potentially escalating conflicts and endangering innocent lives. The weaponization of AI, when used to target specific individuals or groups, blurs the lines between combatants and civilians, posing ethical dilemmas and increasing the risk of violence.
5. Accountability:
Establishing mechanisms for accountability is crucial to hold individuals responsible for the use and outcomes of AI systems. Fostering a culture of responsibility reduces the risks associated with unethical implications of AI and ensures that those deploying AI are held accountable for its impact.
6. Independent Oversight:
Implementing independent oversight is necessary for the responsible development and utilization of AI systems. Involving various stakeholders, including experts, policymakers, and the public, ensures checks and balances, preventing potential misuse and fostering ethical practices in the evolving landscape of AI technology.
Check our blog on Chat GPT for Productivity.
Conclusion
Implications of AI span a vast landscape, from revolutionizing healthcare and industry to triggering ethical considerations. As we navigate the era of AI, its transformative power demands a thoughtful balance between innovation and responsibility, ensuring a future where the implications of AI contribute positively to society.