AI Agents vs. Traditional Programming
Artificial Intelligence (AI) agents are rapidly transforming how we design and interact with technology, marking a clear departure from traditional programming methods. Unlike conventional systems that rely on explicit instructions, AI agents act autonomously, learning and adapting to user needs, making them ideal for complex, dynamic applications. This article unpacks the core principles, operations, benefits, and future of AI agents, presenting a comprehensive look at why they’re reshaping the future of programming.

The Core of AI Agents and Agent-Oriented Programming
At the heart of AI agents lies autonomy—they are self-governing systems that can make decisions, execute actions, and design workflows independently. These systems extend beyond simple task automation by continuously learning from interactions, responding to real-time inputs, and managing intricate environments with limited or no supervision. The foundation of many AI agents is powered by Large Language Models (LLMs), which provide the linguistic capabilities necessary to understand, process, and respond to complex user queries in natural language.
Also read: Robot Vs Human Interaction
Complex user queries in natural language.
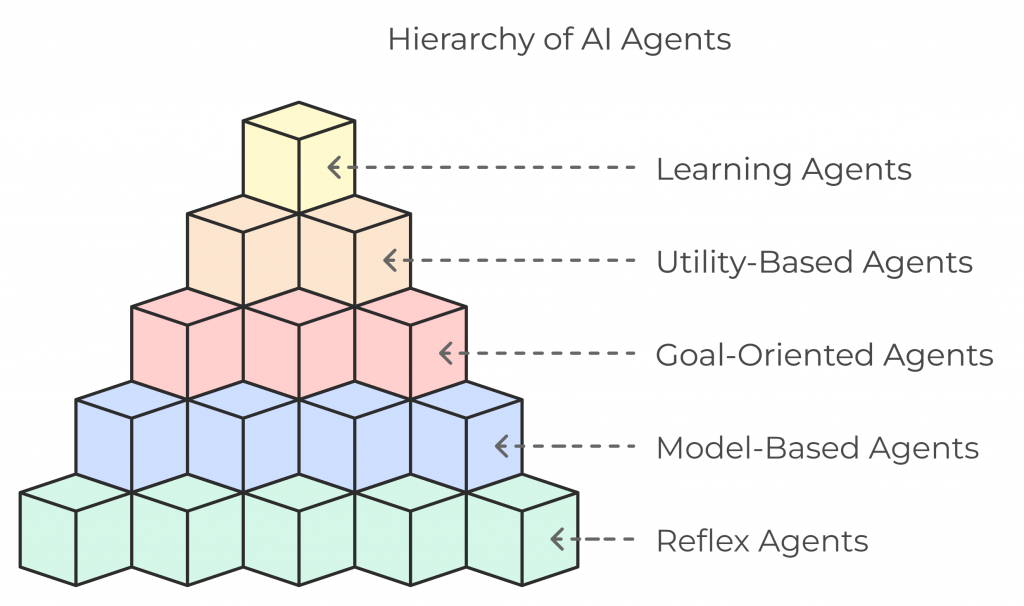
In agent-oriented programming (AOP), AI agents can be designed as simple reflex agents (which operate based on immediate perceptions), model-based agents that maintain an internal environment state, or more complex agents that set and achieve specific goals. There are even utility-based agents that consider the best pathway to success, factoring in elements like risk and reward for each decision. Learning agents, the most advanced type, incorporate feedback to adapt their behavior over time, an approach that has huge implications for fields requiring adaptability, such as healthcare, finance, and customer service.
How AI Agents Work
Unlike static traditional programs, AI agents work in cycles of goal-setting, planning, and adapting. For instance, an AI agent tasked with finding the best time for a surfing trip to Greece would not just look up generic information but would instead combine weather data, user preferences, and expert insights to determine the optimal travel dates. This workflow involves setting a clear goal, sourcing information from a variety of tools, reasoning through the data, and finally recommending the best solution.
These agents utilize tool-calling capabilities, enabling them to pull in real-time information, make informed decisions, and optimize workflows without predefined steps. As agents collect data, they store valuable insights and can adjust future actions accordingly. This constant cycle of setting goals, executing plans, and analyzing feedback makes AI agents particularly efficient and versatile.
Advantages of AI Agents Over Traditional Programming
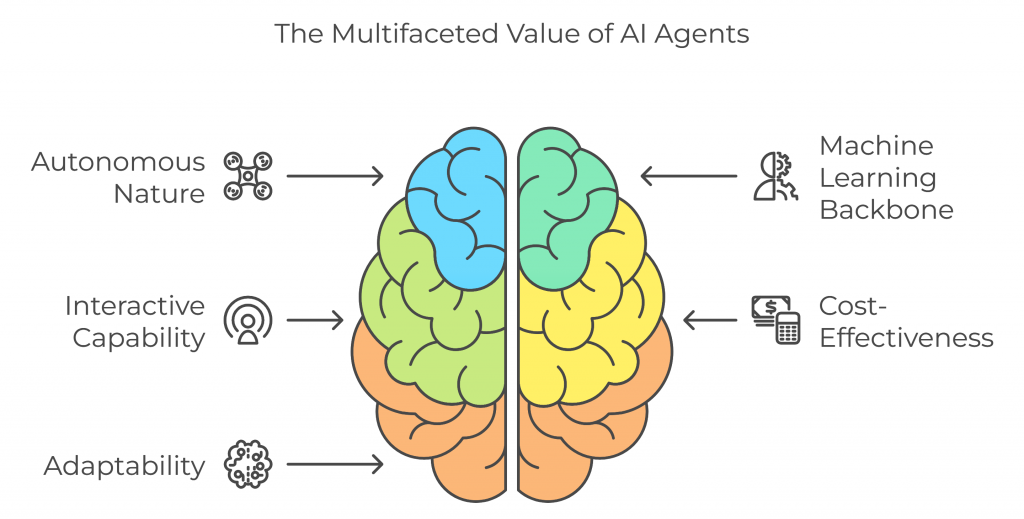
AI agents bring a unique value proposition by minimizing the need for explicit programming and human intervention. Their autonomous nature allows them to learn from experience, deliver interactive responses, and scale to handle high-volume tasks. With machine learning as a backbone, these agents become smarter and more efficient, making them ideal for environments that are data-rich and dynamically evolving.
Another key advantage is their interactive capability, which enhances user experience by providing real-time, personalized responses. In areas like software testing, AI agents excel, ensuring comprehensive coverage, catching edge cases, and executing tests far faster than manual processes. They also adapt to new code changes without needing frequent script updates, making them cost-effective and resource-efficient.
This self-sustaining adaptability makes AI agents a natural fit for applications where data is constantly changing or where interaction is key, such as customer support, supply chain management, and intelligent tutoring systems.

Key Differences from Traditional Programming
The shift from traditional programming to agent-oriented AI is fundamental. While traditional programming relies on predefined rules, AI agents use data-driven learning to adapt and evolve. Unlike static programs, AI agents are dynamic, continually updating their responses based on real-time data, feedback, and user interactions. This ability to learn from data and experience enables AI agents to make decisions on the fly, respond to complex situations, and improve performance without requiring explicit reprogramming.
For example, a traditional program might follow a simple decision tree when prompted, while an AI agent can weigh probabilities, analyze patterns, and generate a response tailored to the current context. The shift from explicit coding to implicit learning marks a departure from rule-based systems, enabling agents to reason and adapt like autonomous entities.
AI agents also possess various levels of sophistication, from reactive agents responding directly to environmental cues, to goal-oriented agents that plan and strategize, and finally to utility-based and learning agents that optimize for long-term success and continuous improvement.
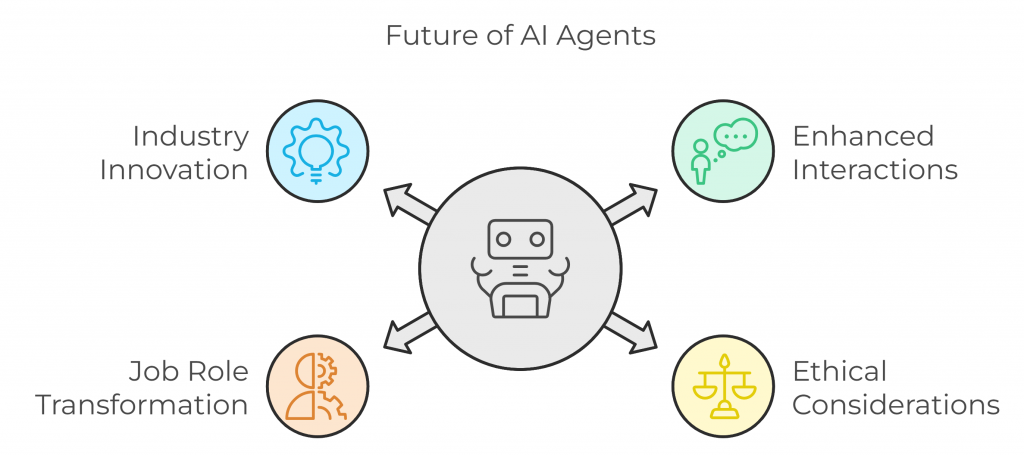
The Future of AI Agents: Transformative Potential
The future of AI agents is promising, with advancements in Natural Language Processing (NLP) expected to enhance the quality of interactions. As these agents become more conversational, the gap between human and machine understanding will narrow, allowing users to communicate naturally with AI systems. Coupled with robotics, AI agents will drive a new wave of intelligent, context-aware machines capable of performing physical tasks with precision and adaptability.
Furthermore, seamless integration into existing software systems is set to make AI agents a core component of digital infrastructure, empowering businesses across industries. However, as AI agents become more pervasive, ethical considerations like transparency, bias prevention, and accountability will become increasingly important. To address these concerns, regulatory frameworks are being developed to ensure responsible AI deployment, while researchers explore new methods to make agent decision-making more explainable and trustable.
Another significant shift will be the transformation of job roles. As AI agents take on repetitive or data-intensive tasks, they will allow professionals to focus on higher-value, strategic activities. This shift demands proactive workforce upskilling and collaboration between humans and AI to maximize productivity. For industries ranging from healthcare to finance, AI agents present opportunities to innovate, personalize services, and drive operational efficiency.

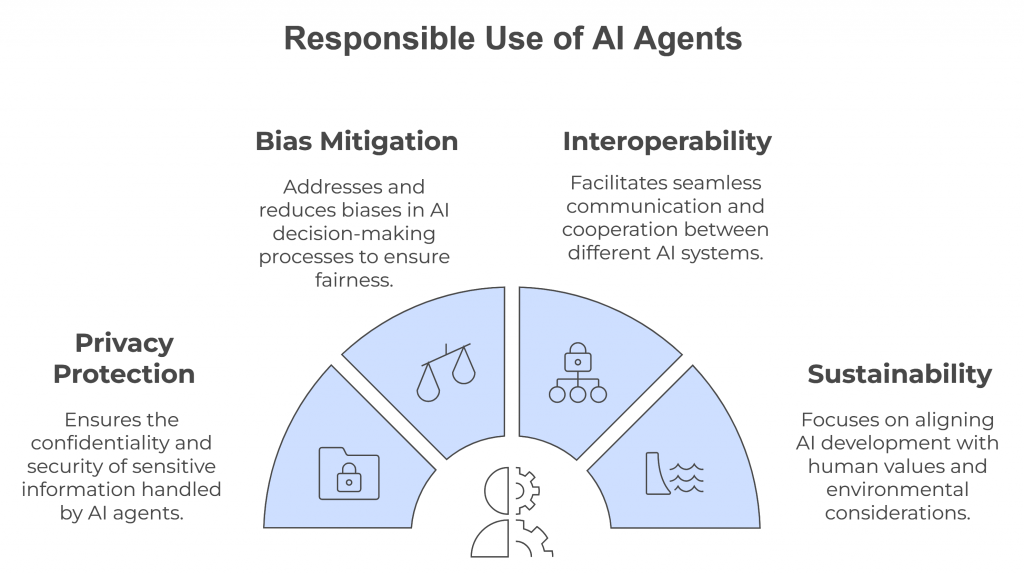
Additional Considerations for Sustainable AI Development
As AI agents progress, certain considerations are paramount for their responsible use. Privacy protection and data security are essential, given that these agents often handle sensitive information. Mitigating biases in AI agents’ decision-making processes is also critical, especially in fields with direct human impact, such as hiring or lending.
Interoperability will be key in a future where multiple AI systems work together across different platforms and applications. Fostering cross-platform communication will create a unified ecosystem that maximizes the value of AI agents. Lastly, focusing on the long-term sustainability of AI agent development will ensure that they remain aligned with human values, societal needs, and environmental considerations.

Conclusion
The transition to AI-driven agent-oriented programming reflects a new era in computing. With their autonomous, adaptive, and interactive capabilities, AI agents have the potential to reshape how we engage with technology, making it more efficient, responsive, and human-centered. This transformation, however, calls for thoughtful regulation, ethical considerations, and an openness to new possibilities.
As we stand on the brink of a future defined by AI agents, the journey is just beginning, with immense potential for innovation, enhanced productivity, and meaningful human-AI collaboration. The question is not whether AI agents will change our digital landscape but how we can harness their potential responsibly and sustainably for the next generation.