Top 5 Methods for Data Protection for small businesses
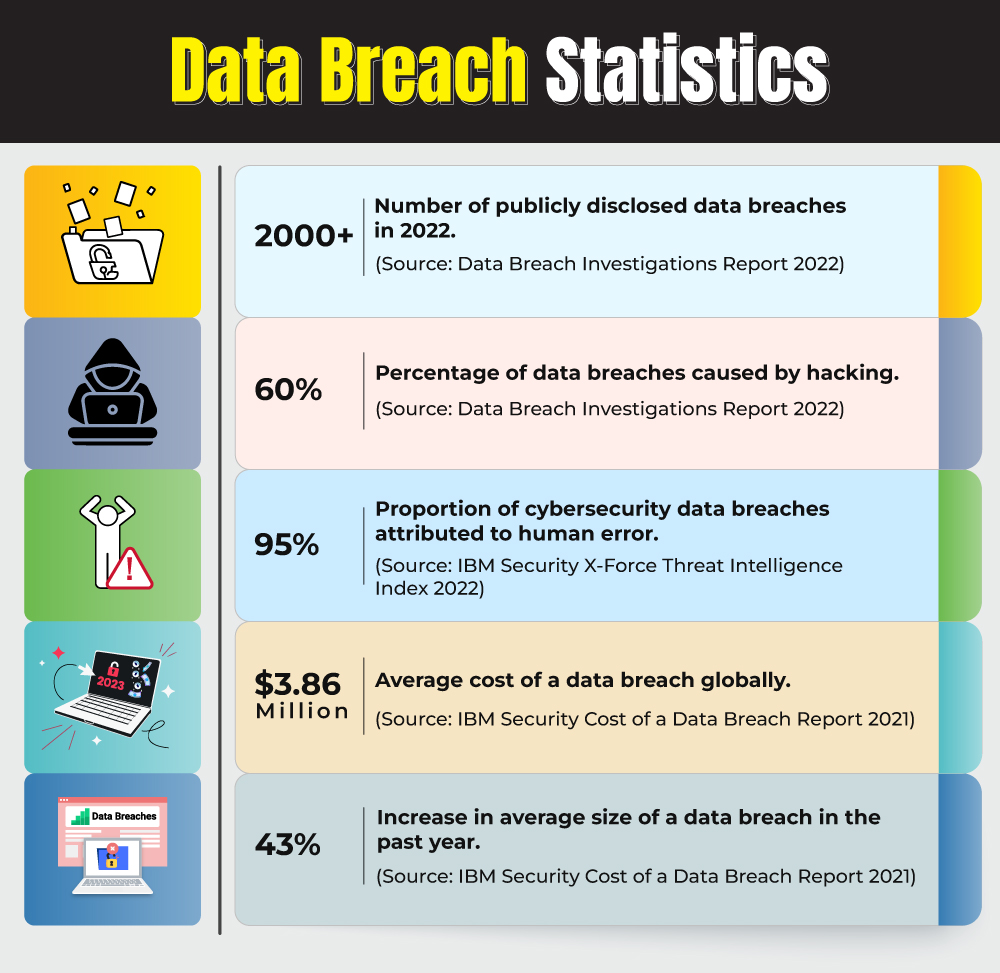
In today’s digital era, data protection is a critical concern for individuals, businesses, and organizations of all sizes. With over 2000 publicly disclosed data breaches in 2022 alone, a significant portion of which resulted from hacking, the risks of financial and reputational damage, compromised data, and legal liabilities are ever-present. To mitigate these risks, several effective methods have been developed to safeguard data from unauthorized access and manipulation. Here, we delve into the top five methods of protecting data.

1. Encryption: A Key Method for Data Protection
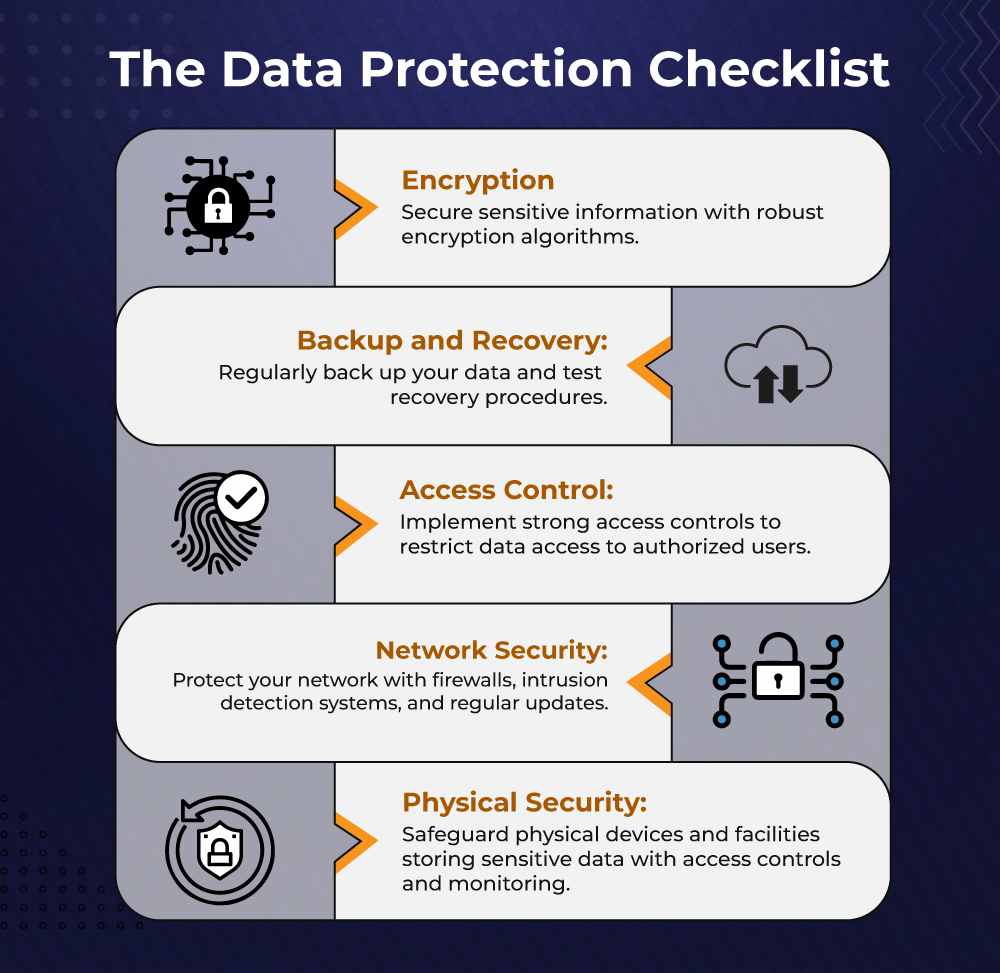
Encryption is a cornerstone of data protection. It involves converting sensitive information into a coded form that is unreadable without the proper decryption key. This ensures that even if data is intercepted or stolen, it remains useless to unauthorized users. Popular encryption algorithms like AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) are employed to scramble data, making it virtually impossible to decipher without the correct key.
Benefits of Encryption:
High Level of Security: Encryption provides a robust security layer that makes data unreadable to anyone without the decryption key. Even if data is intercepted during transmission or stolen from storage, it remains protected.
Regulatory Compliance: Encryption helps organizations comply with various data protection regulations and standards, such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), and PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard).
Challenges of Encryption:
Key Management: Effective encryption requires careful management of encryption keys. If keys are lost or stolen, the encrypted data becomes inaccessible even to the rightful owner.
Algorithm Updates: Encryption methods must be regularly updated and maintained to stay ahead of emerging threats. Outdated encryption algorithms may become vulnerable to attacks.
2. Backup and Recovery: Essential for Data Protection
Regular data backups are vital for preserving information in case of data loss or corruption. By creating copies of data and storing them securely, organizations can quickly recover their information following a disaster. The 3-2-1 backup method—keeping three copies of data on two different local devices and one off-site—provides a robust strategy.
Benefits of Backup and Recovery:
Rapid Recovery: Ensures that data can be quickly restored in the event of loss or corruption, minimizing downtime and disruption to operations.
Data Integrity: Backup and recovery solutions can restore data to a previous state, effectively undoing any unauthorized changes, deletions, or corruptions.
Challenges of Backup and Recovery:
Secure Storage: Backups must be stored in secure locations to protect against theft, natural disasters, and other risks. This often involves off-site storage solutions.
Regular Testing: Backup systems must be tested regularly to ensure that they can be successfully restored when needed. This involves performing regular restore tests to validate the backup data.
3. Access Control: Protecting Data from Unauthorized Access
Access control restricts access to sensitive information to only authorized users. Methods such as passwords, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and role-based access control (RBAC) ensure that only individuals with proper authorization can access specific data.
Benefits of Access Control:
Accountability: Access control systems track and log user activities, providing a record of who accessed what data and when. This enhances accountability and can help detect and investigate unauthorized access.
Efficiency: Role-based access control (RBAC) simplifies the management of access permissions, allowing administrators to assign roles with predefined access levels. This reduces the complexity of managing individual user permissions.
Challenges of Access Control:
Implementation: Access control systems require robust implementation, including the use of strong, unique passwords and MFA. Poorly implemented access controls can be easily bypassed.
Maintenance: Access control systems must be regularly updated and audited to ensure they remain effective. This includes reviewing access permissions and ensuring that only authorized users have access to sensitive data.
4. Network Security: Safeguarding Data in Transit
Network security encompasses measures to protect information and assets on computer networks from unauthorized access, theft, or damage. This includes using firewalls to block unauthorized access, implementing intrusion detection systems (IDS) to monitor for and prevent cyber-attacks, and using encryption for data transmitted over the network. Regular software updates and employee training are also crucial.

Benefits of Network Security:
Confidentiality: Network security measures help ensure that sensitive information remains confidential and is not accessed by unauthorized parties.
Compliance: Effective network security helps organizations meet regulatory requirements and industry standards, such as HIPAA and PCI DSS.
Risk Management: Network security practices help identify and mitigate potential security risks, reducing the likelihood of breaches and other incidents.
Challenges of Network Security:
Complexity: Implementing and maintaining network security systems can be complex and requires specialized knowledge and expertise.
Continuous Improvement: Network security measures must be continuously updated and improved to keep pace with evolving threats and new attack methods.
5. Physical Security: Protecting Data at the Source
Physical security involves measures to secure physical devices and facilities storing sensitive information. This includes secure storage cabinets, access control systems with biometric authentication, security cameras, and alarms.
Benefits of Physical Security:
Confidence: Physical security measures provide assurance that sensitive data is protected from physical theft and unauthorized access.
Cost Reduction: Effective physical security can prevent the costs associated with data breaches and loss of physical media, such as backup tapes or hard drives.
Challenges of Physical Security:
Human Error: Despite physical security measures, human error remains a significant risk. For example, employees might misplace or leave backup media unsecured.
Monitoring and Tracking: Ensuring that physical security measures are consistently followed and that backup media is properly tracked and stored requires ongoing effort and vigilance.
Data Protection for small businesses.
The Importance of a Holistic Approach to Protecting Data
The effectiveness of each of these data protection methods increases when they are part of a holistic approach. This approach integrates multiple layers of defense, each complementing the others to create a robust security posture.
Here’s why a holistic approach is crucial:
Synergy: When implemented together, these methods reinforce one another, enhancing overall security. For example, encryption provides an additional layer of protection to backup data, further safeguarding it from unauthorized access.
Comprehensive Coverage: Different threats may exploit vulnerabilities at various points in the data lifecycle. A holistic approach ensures that no aspect is left vulnerable, covering data at rest, in transit, and during backup and recovery processes.
Resilience: In the face of evolving cyber threats, a multi-layered approach increases resilience. Even if one layer is compromised, others remain intact, minimizing the impact of security breaches.
Regulatory Compliance: Many data protection regulations require a multi-faceted approach to security. By adopting a holistic strategy, organizations can better meet compliance requirements and avoid penalties.
Adaptability: The digital landscape is constantly evolving, with new threats emerging regularly. A holistic approach allows organizations to adapt their security measures to address new challenges effectively.
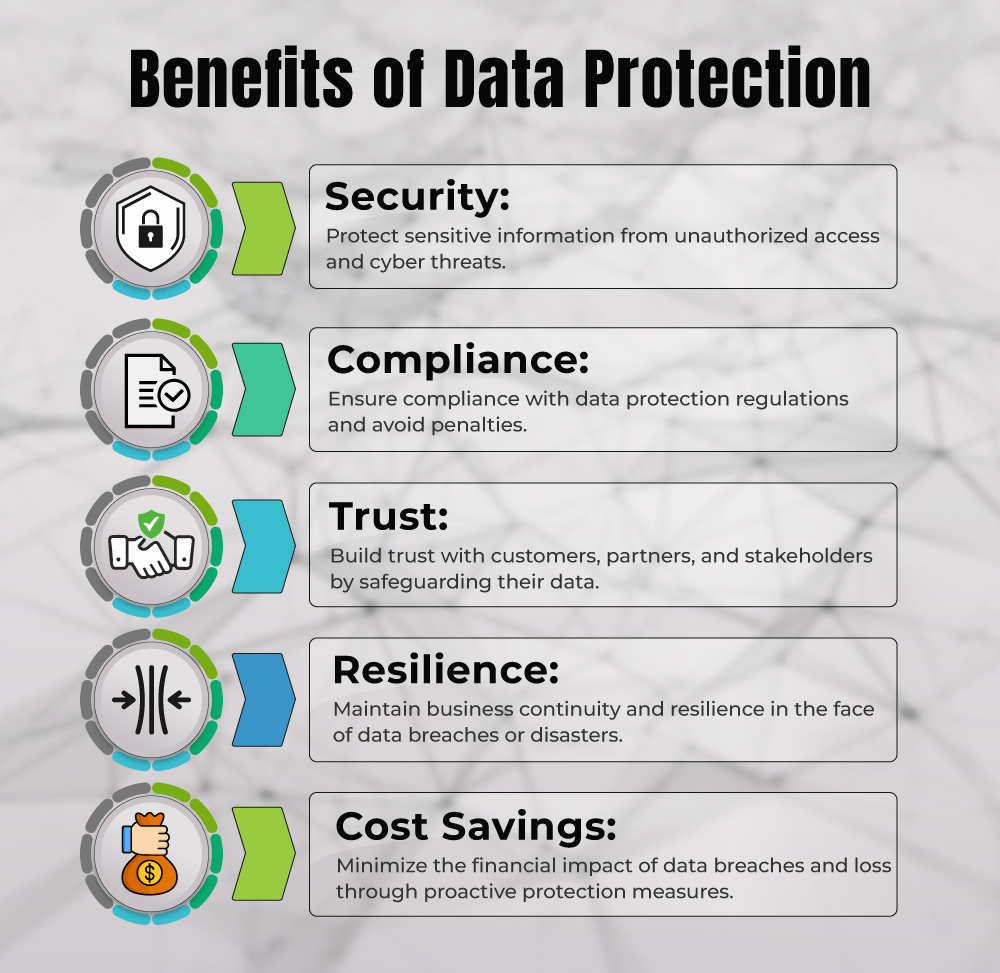
By adopting a holistic approach to data protection, organizations can enhance their security posture, mitigate risks, and safeguard sensitive information effectively.

Take Action Today to Protect Your Data
In today’s digital age, the protection of data is paramount. Don’t wait until it’s too late—take proactive steps to safeguard your information now. Whether you’re an individual, a small business, or a large organization, implementing robust data protection measures is essential for safeguarding your assets and maintaining trust with stakeholders.
Remember, data breaches can have far-reaching consequences, including financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities. By prioritizing data protection and adopting a holistic approach, you can minimize these risks and ensure the security and confidentiality of your sensitive information.
Share and Spread Awareness About Data Protection
Spread the word about the importance of data protection by sharing this article with your network. Together, we can raise awareness and empower individuals and organizations to take proactive steps to protect their data. Let’s work together to create a safer and more secure digital future for all!
Conclusion
In conclusion, data protection is a critical concern in today’s digital landscape. A comprehensive approach, incorporating encryption, backup and recovery, access control, network security, and physical security, can significantly enhance the security and confidentiality of sensitive information. Regular assessment and updating of security measures are essential to keep pace with technological advancements and evolving threats.