Understanding the key difference between SaaS and cloud
We know that SaaS is synonymously called cloud. But are the two actually the same? Is there a key difference between SaaS and cloud? We are going to find out. After all, the global cloud-managed service market is set to grow to 130.1$ billion by 2028, according to a new study by SkyQuest.
The report further states that 65% of enterprises will use cloud-based services by 2025. Where dominant market use will be in North America, Europe, then Asia-Pacific (around 61%).
The reason that is emerging from this growing dependency on the cloud is its efficiency in piles of data storage, flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and, most importantly, disaster recovery. If the umbrella of cloud is in high demand, then summing it all to SaaS may be a more significant claim. Therefore to understand the situation better, we elucidate our discussion on the following lines:
- What is the difference between SaaS and the cloud?
- What are the different types of Cloud services?
- SaaS
- IaaS
- PaaS
- BPO
- How is cloud computing deployed?
- Public cloud
- Private cloud
- Hybrid cloud
- Multi-cloud
- Applications of cloud computing
What is the difference between SaaS and the cloud?
Back to our very first claim, SaaS is synonymous with the cloud. And nobody disagrees with the claim. Because service SaaS or Software as a service is a component of the cloud. More so, SaaS is an application-based service under the large umbrella of cloud computing. Which also includes cloud services of,
Iaas (Infrastructure as a service)
and Paas( Platform as a service).
A SaaS-based application is something you run via a web browser hosted in the cloud. It is not a plugin but an application given to you by the provider as an end-user product.
Cloud-based service or product requires you to access the internet connection to carry out a service. Therefore the term we are looking at here is cloud computing, the umbrella for the word cloud. Where IT resources are provided over the internet on-demand, and you pay as per use.
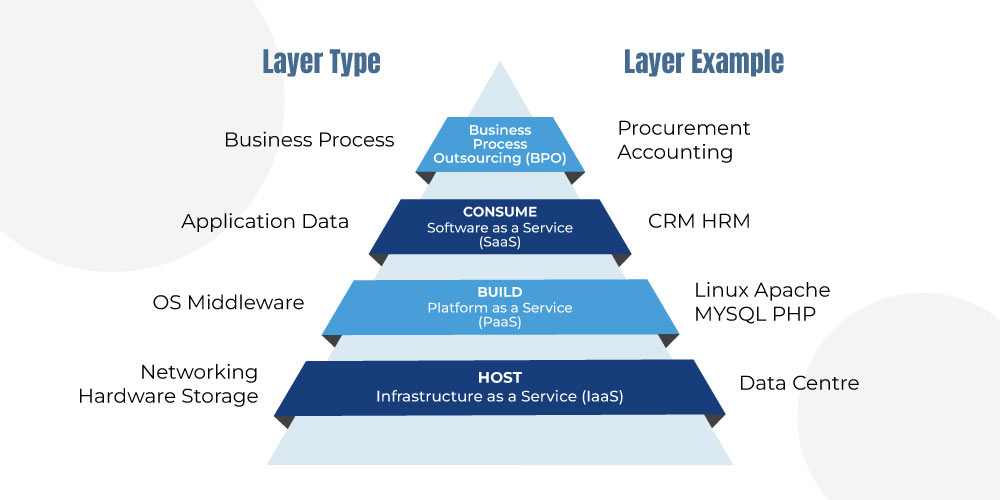
Here’s an example to help you clearly understand cloud computing and its types of services:
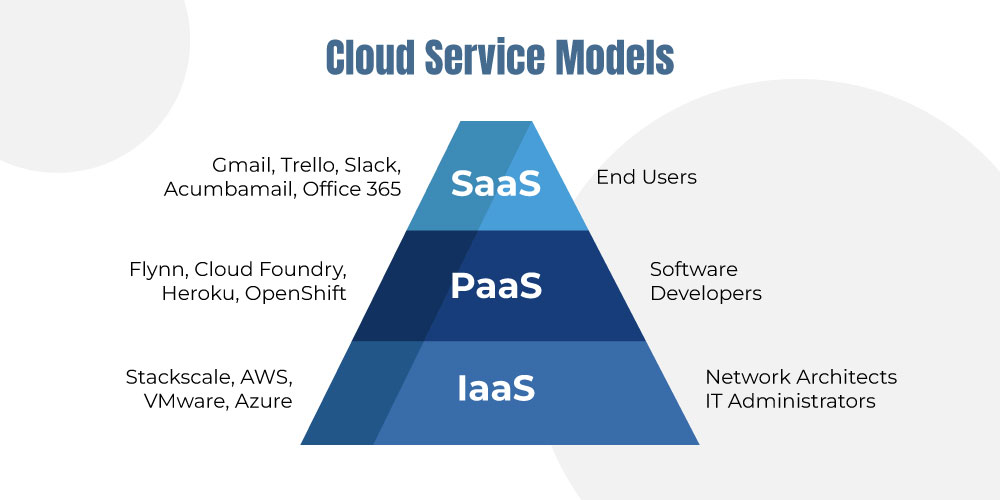

What are the different types of cloud services?
In our discussion above, we learned what cloud computing is and how SaaS is a service under its umbrella. We also briefly mentioned the other two types, IaaS and PaaS. But these are the predominant type of BPO (Business Process Outsourcing).
IaaS
IaaS or Infrastructure as a cloud is a cloud computing service that delivers IT infrastructure like storage resources, network, and fundamental compute (software and objects related to computation of software). It is a collective term for all the necessary computational resources to run a program successfully.
The physical infrastructure is needed to run the IT systems and applications. The infrastructure is hosted in a private or public cloud and is fully managed by the provider.
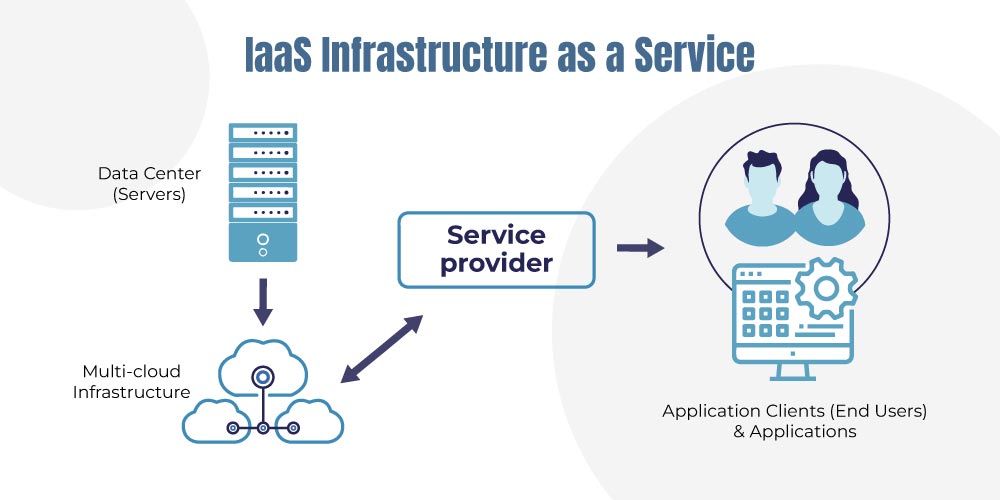

Companies rent servers for storage and computing in the cloud.
It is a flexible model that allows you to:
- Monitor performanceik
- Configure policies that automate infrastructural tasks like balancing of lad and backup
- Monitor and view and system logs
- Implement security measures for the infrastructure.
In addition, the types of IaaS include compute (CPU), storage, and networking(routers/ switches).
PaaS
Paas, or Platform as a service, is another cloud computing service that provides hardware and software application infrastructure for maintaining and developing applications. Where the cloud provider will control the hardware and software in their database. This also makes it a comparatively cheaper option compared to On-premise infrastructure.
The design of PaaS supports the complete lifecycle of a web application, i.e., from
- Building
- Testing
- Managing
- Deploying
- Updating.
With PaaS, you only manage and develop the services/ applications you want. The rest of everything lies with the provider.
It is typically used for:
- Analyzing and mining data
- Finding insights and patterns
- Providing the framework for developers to work upon,
- Providing additional services like directory, workflow, and security.
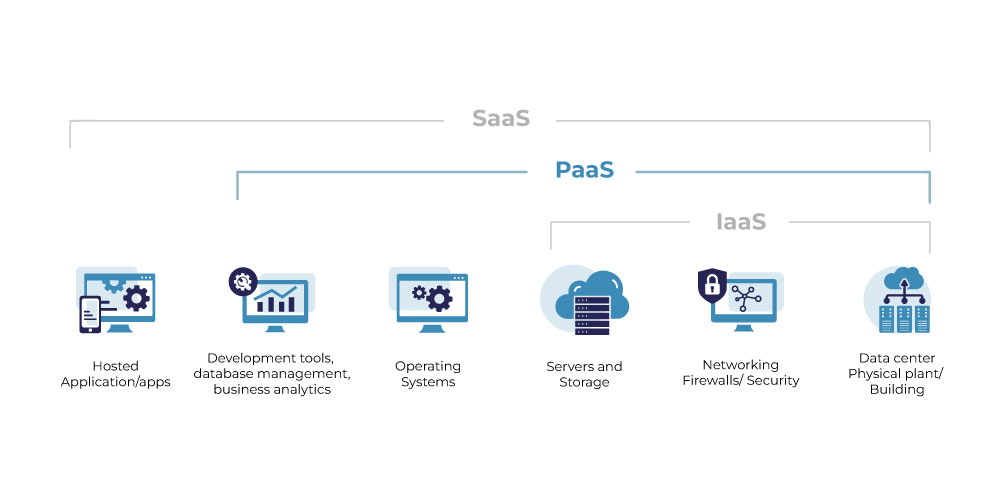

Apart from these two known service types, there is another service type in cloud computing.
BPO
BPO or Business Process Outsourcing forms the topmost layer of the cloud. Although it doesn’t involve the technology through and through like the ones discussed above. It is in the group because it is a business model like the rest. Where you outsource services/ business processes to a vendor to achieve organizational goals. The BPO segment employs cloud services for better flexibility and agility. So it is not a cloud but a similar type of business model like a cloud.

How is cloud computing deployed?
All this while, we discussed the types of cloud services one can undertake or utilize for their business. An important aspect of it that we haven’t touched is the way it gets deployed for usage. I mean, that’s crucial, right? How will one go about the services without their deployment? So this section will help you learn those types.
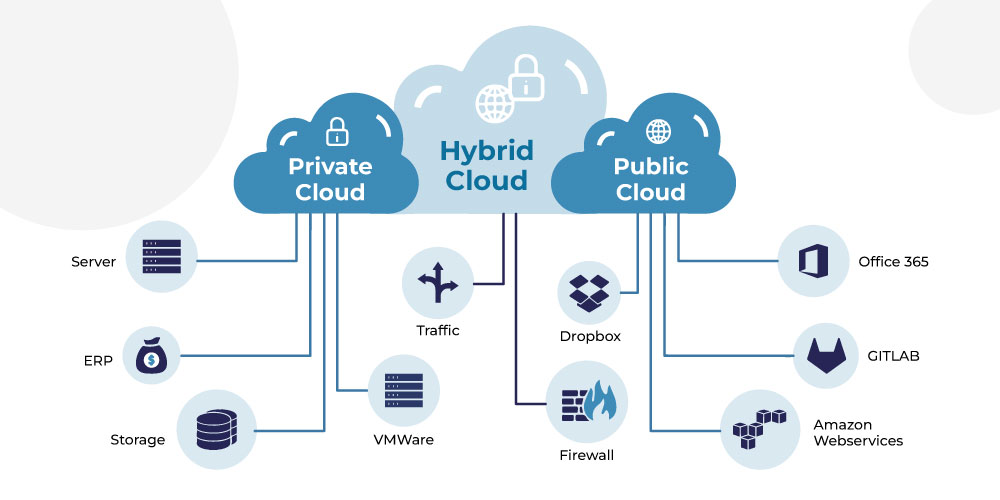

Public Cloud
Public cloud is from the IT infrastructure that any end user does not own. An example to help you better understand this are Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and IBM cloud.
They are today provided on clients’ on-premise data centers making ownership and location differences outdated.
What makes it public is the multiple partition redistributions to many owners for use. And are often brought in use for low-sensitive applications that demand diverse resources.
Private Cloud
These are cloud environments dedicated only to a single end-user/ group. Where the cloud environment runs on the user’s firewall with remote access. Among these are two further bifurcations:
Managed private cloud:
It is managed by a third-party vendor and provided to you.
Dedicated cloud:
A dedicated cloud segment for a unit within another cloud.
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud has the best of both worlds. Where a bit of each private cloud and public cloud is in use for functionality. It is a single unit created from multiple departments and connected via LANs, APIs, VPNs, or WANs.
Any and every system can become a hybrid cloud where apps can move in and out of many separate and connected environments.
Multi-Cloud
Multicloud is a system where multiple clouds are in use together for efficient working. Their usual employment is to protect sensitive data. Multiple clouds can become a hybrid cloud when all of it gets integrated together. But all hybrid is not multi-cloud since it depends on the absence and presence of integration.
Applications of cloud computing
In this segment of understanding the cloud, we discuss the application of cloud computing practically as we now have an idea of its types and deployment models.
Data Storage,
One of the most widely known applications of cloud computing is its ability to data storage. This comes as a savior for the enormous data piles that accumulate and need multiple storage resources.
E-commerce application
In this era of online shopping, e-commerce has gained significant momentum with the ease cloud provides in its operational systems, customer data, and minimum time requirement in handling.
Education
Thanks to cloud computing advancements, today’s education sector is also taking advantage of the learning atmosphere. From students to teachers and learning materials, cloud computing is helping connect over distance and learn better with aided tech support.
Web application for anti-virus
Gone are the days when the only way to guard your data was to install anti-virus software. The advent of the cloud has led to cloud anti-virus software that detects faults or viruses in the organization’s system and fixes it.
Development and Testing
Cloud computing offers the easiest way to test products. Since its flexible, comparatively cheap, and scalable, it provides a feasible environment for testing and development without the hassle of expensive IT infrastructure.
Besides the applications, we mention here, cloud computing employment is in many other work fields., like designing infrastructure, extensive data analysis, recovery and backup, and much more. The scope is ever-growing and expanding.
We may not be able to sum it all up here. But the scope of discussion and suggestion is always welcome. So please feel free to connect with us and share your thoughts with us.